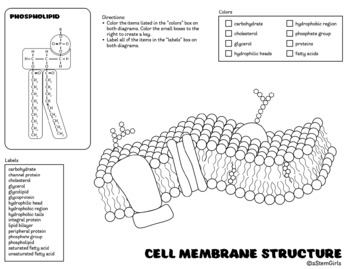
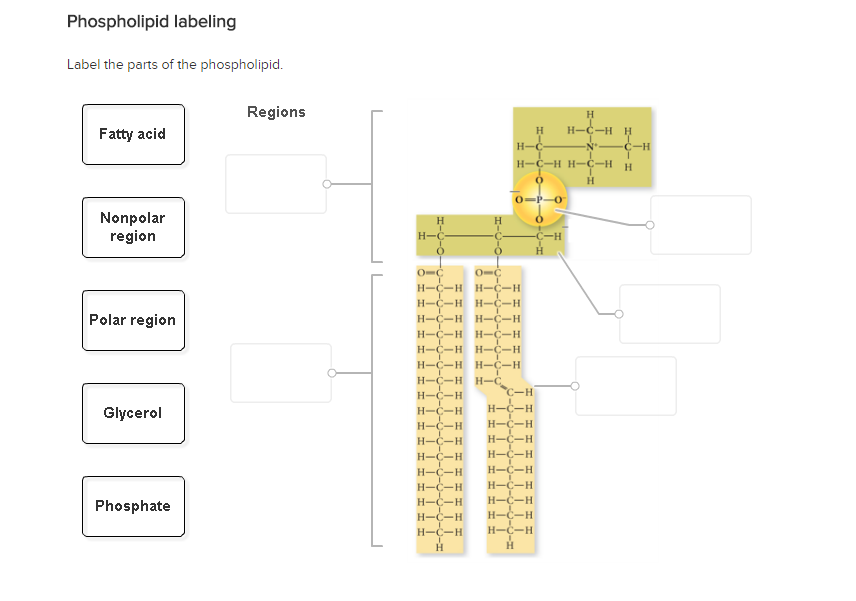
41 phospholipid label
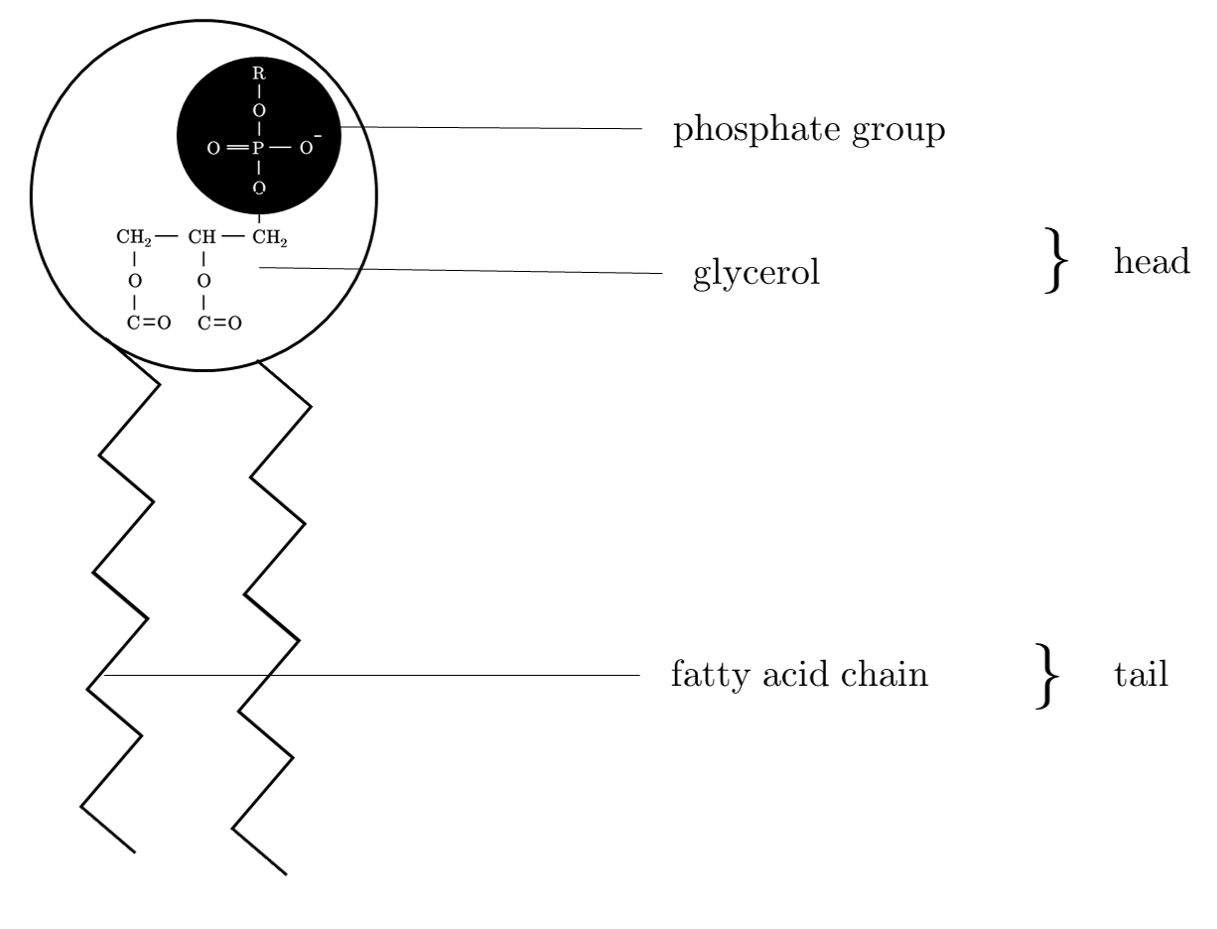
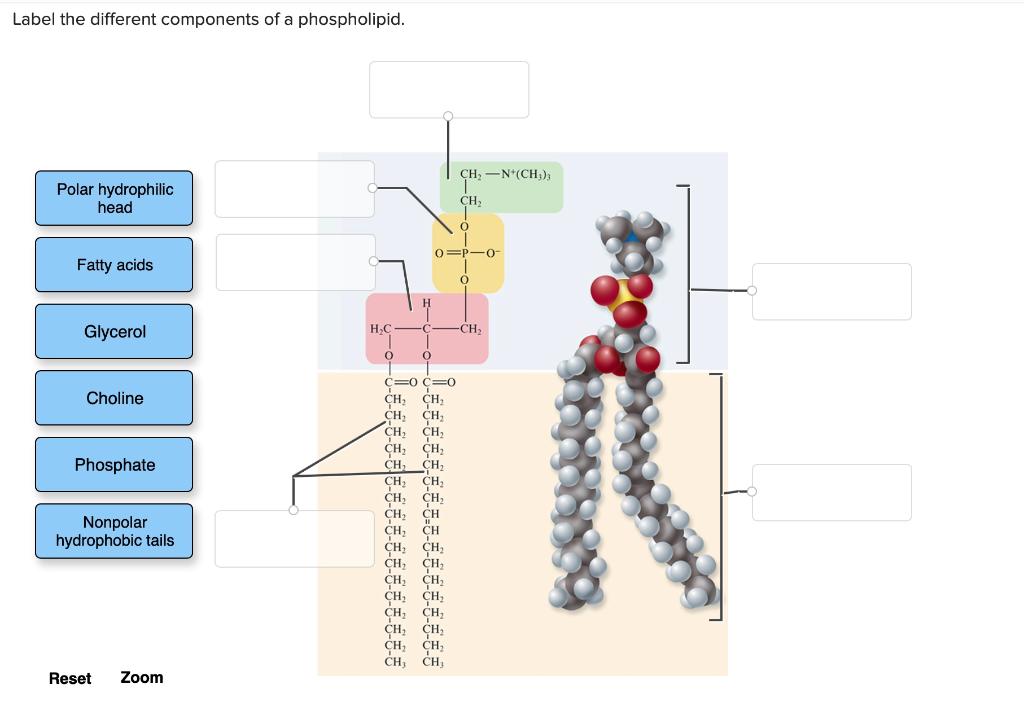
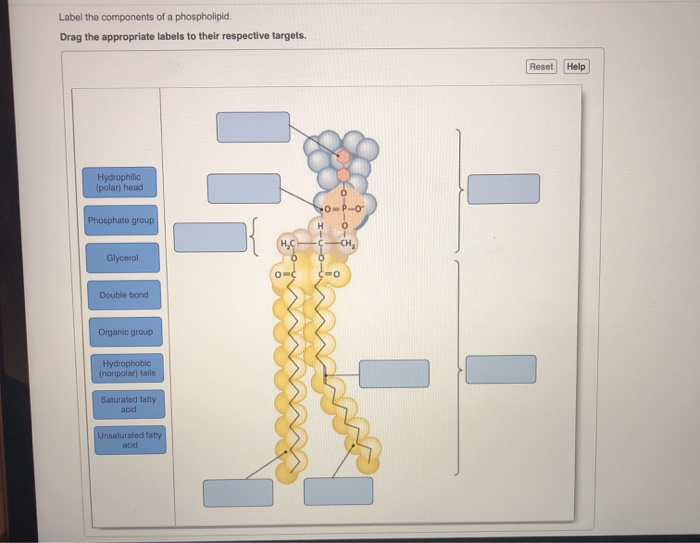
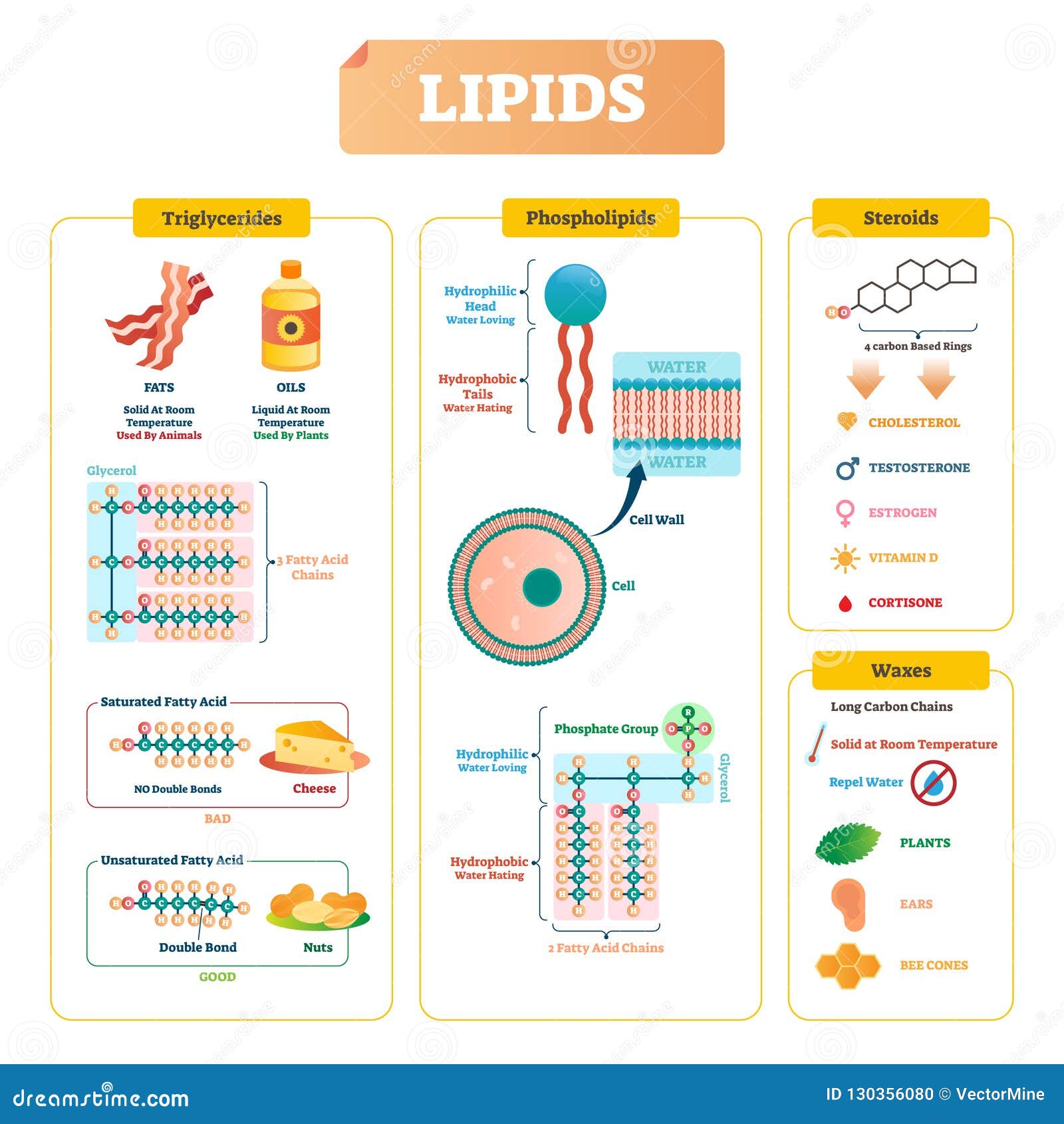
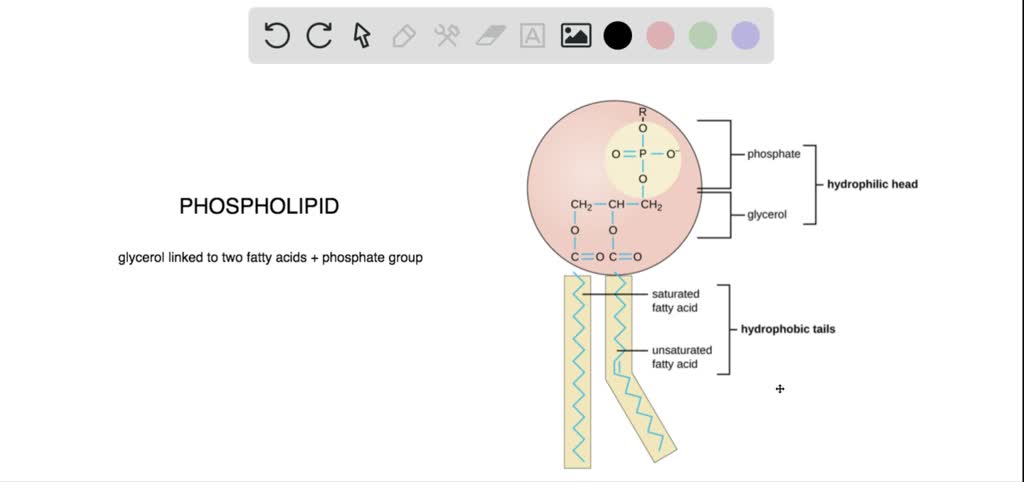
Phospholipid Structure Labeling Diagram | Quizlet Phospholipid Structure Labeling Diagram | Quizlet Phospholipid Structure Labeling + − Learn Test Match Created by njabara Terms in this set (6) Term Phosphate Location Term Glycerol Location Term Saturated Fatty Acid Location Term Unsaturated Fatty Acid Location Term Hydrophobic Tails Location Term Hydrophilic Head Location Phospholipids | Biology for Majors I - Lumen Learning Therefore, phospholipids form an excellent two-layer cell membrane that separates fluid within the cell from the fluid outside of the cell. A phospholipid molecule (Figure 2) consists of a three-carbon glycerol backbone with two fatty acid molecules attached to carbons 1 and 2, and a phosphate-containing group attached to the third carbon.
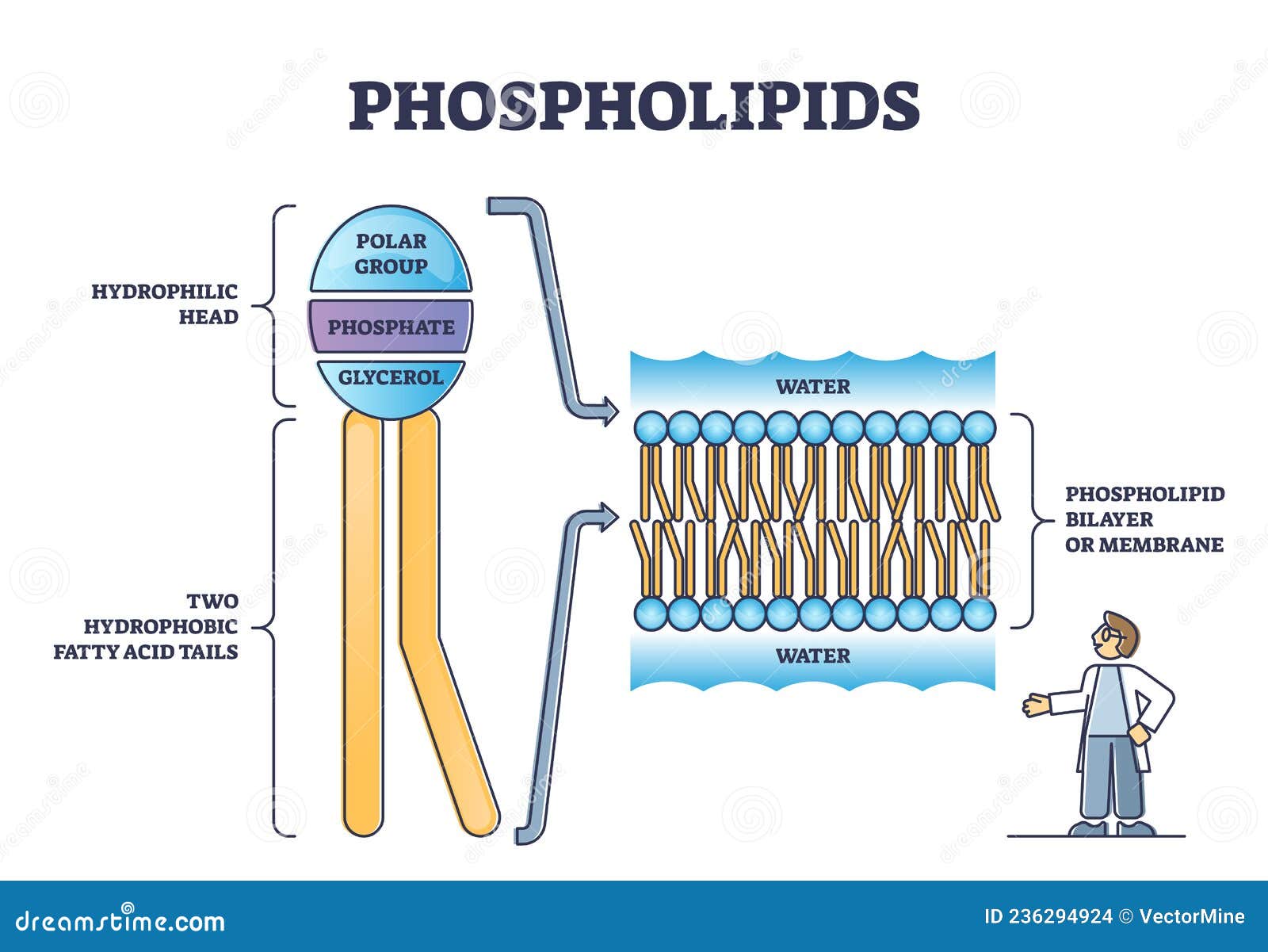
Phospholipid structure (video) | Khan Academy Phospholipids are molecules that form the cell membrane. They consist of a polar phosphate head group and two nonpolar fatty acid tails joined by a glycerol backbone. The phosphate group can link with different molecules, such as serine or choline, to generate diverse kinds of phospholipids.

Phospholipid label
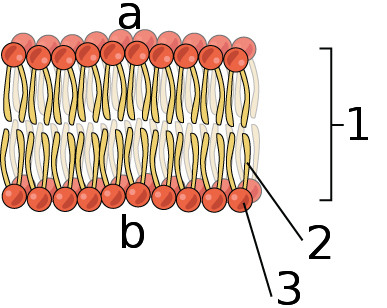
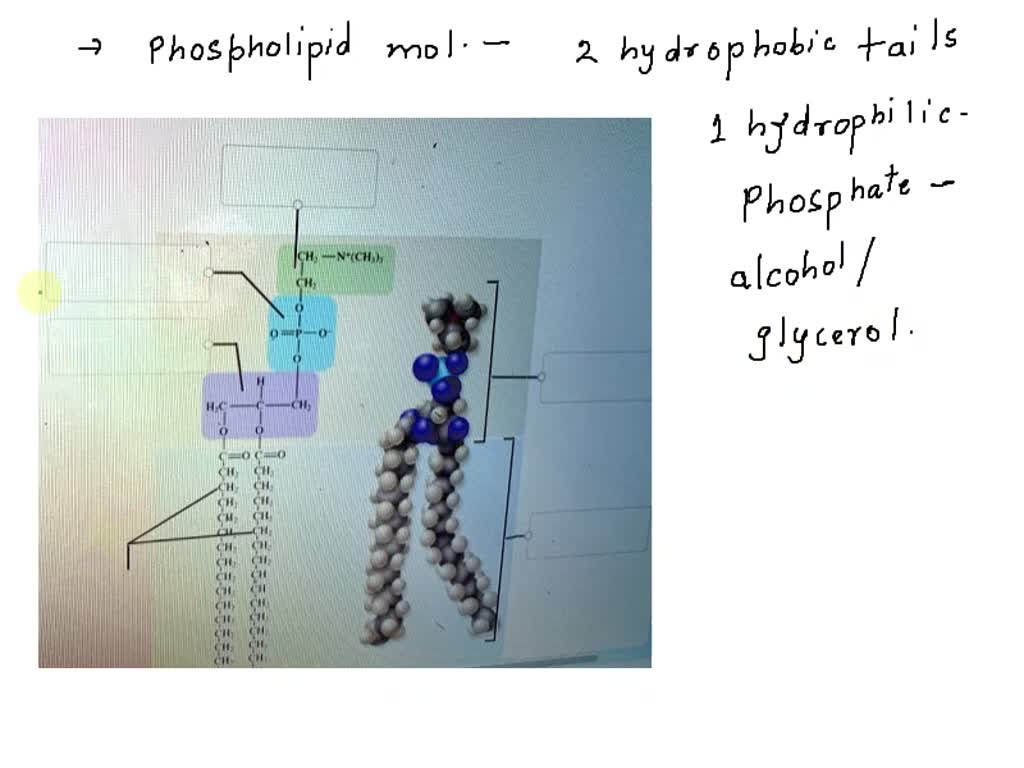
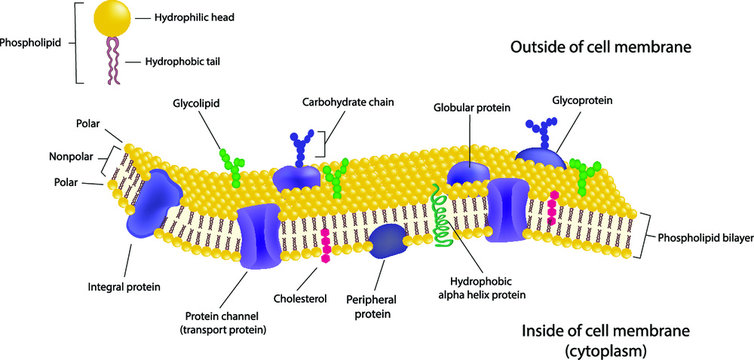
Phospholipids Flashcards | Quizlet Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules that make up the bilayer of the plasma membrane and keep the membrane fluid. what do phospholipids consist of Phospholipids consist of a glycerol molecule, two fatty acids, and a phosphate group that is modified by an alcohol describe the phospholipid head Phospholipid Bilayer | Lipid Bilayer | Structures & Functions Phospholipid Bilayer: All cells are surrounded by the cell membranes, and this characteristic best portrayed by the Fluid Mosaic Model.According to this model, which was postulated by Singer and Nicolson during the 1970s, plasma membranes are composed of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates that are arranged in a "mosaic-like" manner.. The fundamental structure of the plasma membrane is the ... 001727: Phospholipids | Labcorp Abnormal phospholipid levels have been associated with obstructive jaundice, abeta- or hypobetalipoproteinemia, Tangier disease, and LCAT deficiency. 1 Limitations This procedure measures lecithin, sphingomyelin, and lysolecithin phospholipids.
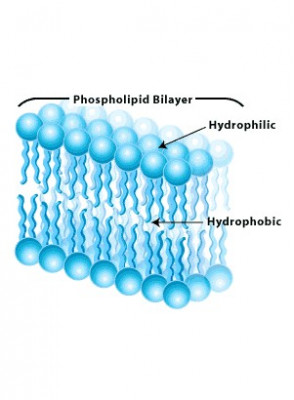
Phospholipid label. Draw and Label a Phospholipid | Lipids | A Level Biology • Draw and Label a Phospholipid | Lipids | A Level Biology Learnbiologynet 2.47K subscribers 4 229 views 10 months ago A Level Biology This short clip from the Lesson "Lipids: - the properties... Labeling phospholipid membranes with lipid mimetic luminescent metal ... There is no information, however, on the physical properties of phospholipid membranes labeled with metallosurfactant luminophores. Here, the use of two lipid-mimetic metallosurfactants, based on well-known structural motifs of luminescent iridium and ruthenium complexes, is proposed for this purpose: [Ru (bpy)2 (dn-bpy)] 2 + and [Ir (ppy) 2 ... Phospholipid | biochemistry | Britannica phospholipid, also called Phosphatide, any member of a large class of fatlike, phosphorus-containing substances that play important structural and metabolic roles in living cells. Structure of the plasma membrane (article) | Khan Academy A phospholipid is a lipid made of glycerol, two fatty acid tails, and a phosphate-linked head group. Biological membranes usually involve two layers of phospholipids with their tails pointing inward, an arrangement called a phospholipid bilayer.
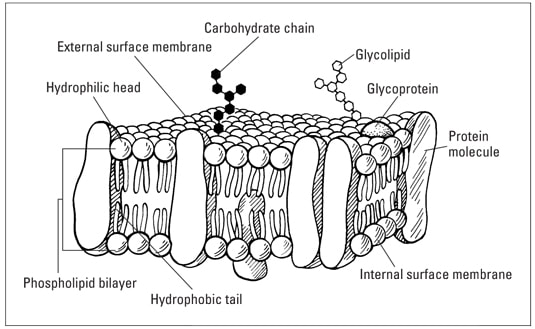
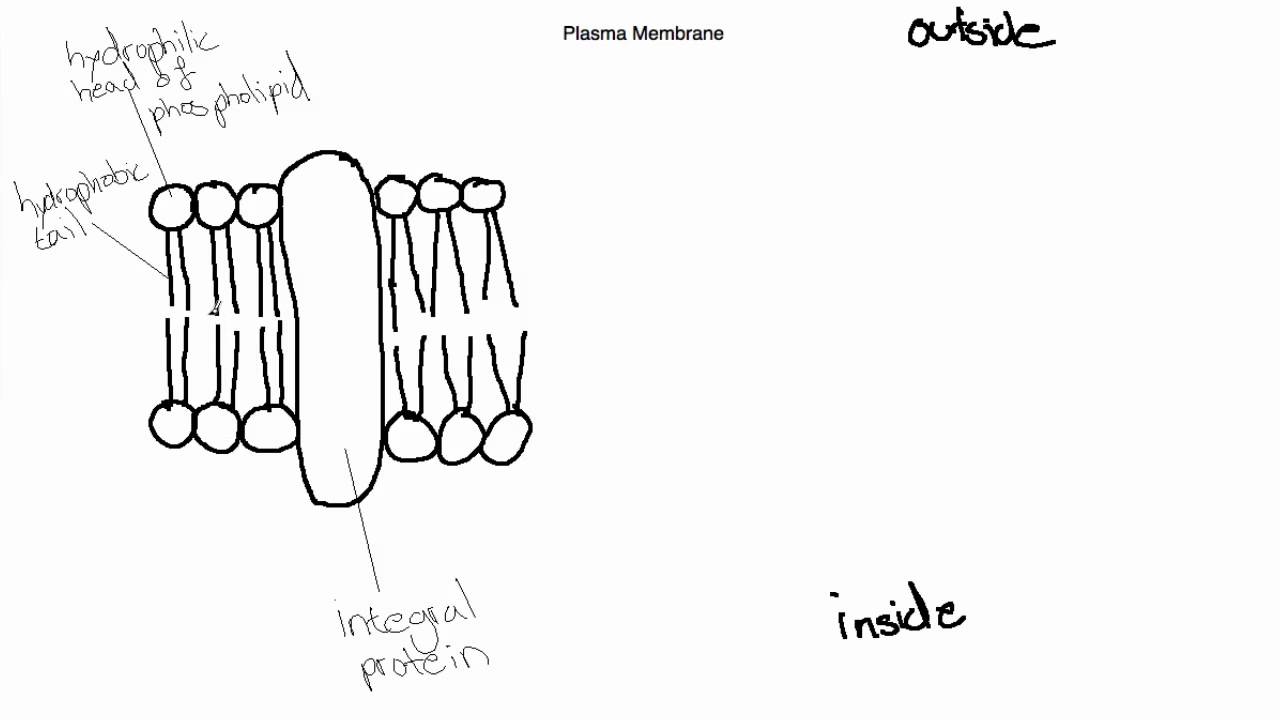
Phospholipid: Definition, Structure, Function | Biology Dictionary A phospholipid is a type of lipid molecule that is the main component of the cell membrane. Lipids are molecules that include fats, waxes, and some vitamins, among others. Each phospholipid is made up of two fatty acids, a phosphate group, and a glycerol molecule. The cell membrane review (article) | Khan Academy Cell membrane. Specialized structure that surrounds the cell and its internal environment; controls movement of substances into/out of cell. Hydrophobic. Molecule that repels water ("water-fearing") Hydrophilic. Molecule that is attracted to water ("water-loving") Amphipathic. Molecule that contains both a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic end. Phospholipid: Definition, Structure, Function, Examples - Science Terms Phospholipid Definition A phospholipid is an amphiphilic molecule consisting of a polar head region, a unit of glycerol, and two or more non-polar fatty acid tails, typically found in a cell membrane. A bilayer of phospholipid molecules forms a plasma membrane. Fluid mosaic model: cell membranes article - Khan Academy There are two important parts of a phospholipid: the head and the two tails. The head is a phosphate molecule that is attracted to water (hydrophilic).The two tails are made up of fatty acids (chains of carbon atoms) that aren't compatible with, or repel, water (hydrophobic).The cell membrane is exposed to water mixed with electrolytes and other materials on the outside and the inside of the ...
001727: Phospholipids | Labcorp Abnormal phospholipid levels have been associated with obstructive jaundice, abeta- or hypobetalipoproteinemia, Tangier disease, and LCAT deficiency. 1 Limitations This procedure measures lecithin, sphingomyelin, and lysolecithin phospholipids. Phospholipid Bilayer | Lipid Bilayer | Structures & Functions Phospholipid Bilayer: All cells are surrounded by the cell membranes, and this characteristic best portrayed by the Fluid Mosaic Model.According to this model, which was postulated by Singer and Nicolson during the 1970s, plasma membranes are composed of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates that are arranged in a "mosaic-like" manner.. The fundamental structure of the plasma membrane is the ... Phospholipids Flashcards | Quizlet Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules that make up the bilayer of the plasma membrane and keep the membrane fluid. what do phospholipids consist of Phospholipids consist of a glycerol molecule, two fatty acids, and a phosphate group that is modified by an alcohol describe the phospholipid head



![Solved] Draw, label, and describe the structure o | SolutionInn](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/questions/2021/04/607d241fb1929_Screenshot2021041818055311.jpg)


















Post a Comment for "41 phospholipid label"